Log Regex Markup
Highlight and Divide Data Using Regular ExpressionsThe Log Regex Markup engine is a unique and highly practical feature of IO Ninja, designed to enhance data log analysis with intuitive visual aids.
This engine uses user-defined regular expressions to automatically—and instantly!—highlight data patterns or insert packet delimiters. It’s powered by Google RE2, one of the world’s fastest and most reliable regular expression libraries.
How Does Regex Markup Improve Data Analysis?
Colorize Key Data
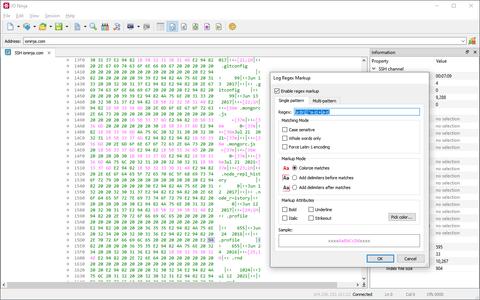
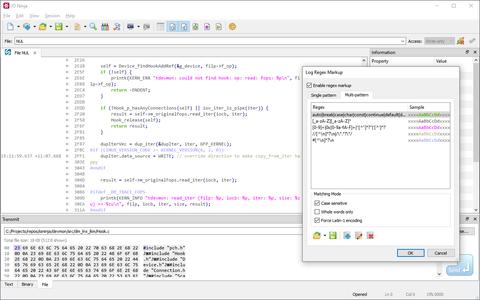
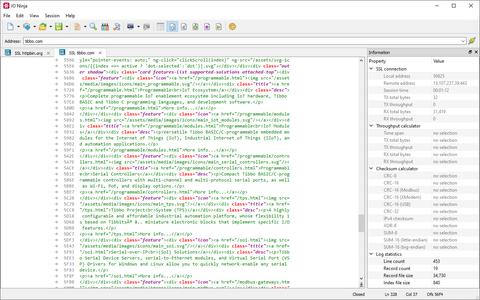
The simplest way to leverage the regex markup feature is by defining regular expressions for important tokens in your protocol and assigning them distinct colors for easy identification.
For example, as shown in the screenshot, all XTERM CSI escape sequences are automatically highlighted in pink.
Packetize Your Logs
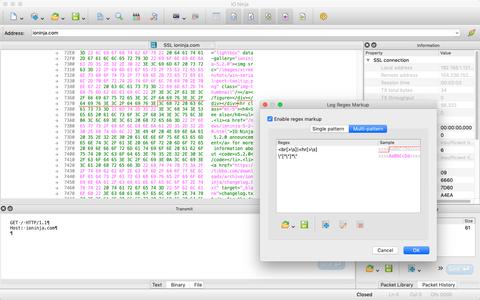
Another powerful use case is defining packet boundaries by inserting delimiters with regular expressions.
For instance:
- If packets in your protocol begin with a specific header or preamble, you can write a regex to match those headers and insert delimiters before each match.
- Similarly, if your packets end with clear terminators, you can create a regex to match those terminators and insert delimiters after each match.
Handle Multiple Rules
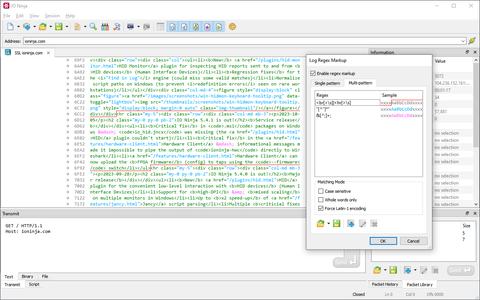
Need to highlight different entities with different colors while simultaneously marking packet boundaries? No problem! With IO Ninja, you can define multiple rules and assign as many colors as needed to annotate everything you want to focus on.
The best part? It’s just as fast as applying a single regex!
Regex Engine Details
The IO Ninja regex engine is DFA-based, unlike the backtracking engines used in PCRE, Python, Ruby, and similar libraries.
While backtracking engines can suffer significant performance drops (sometimes exponentially!) depending on the complexity of the regex and the number of patterns, IO Ninja avoids these pitfalls. No matter how many markup rules or how complex the regular expressions are, the log will always be colorized and packetized FAST.
However, this design choice does come with some trade-offs. IO Ninja doesn’t support certain advanced regex features found in backtracking engines, such as backreferences and named groups.
Syntax
Since the regex markup engine is powered by Google RE2, it supports all the features of RE2. For a full syntax specification, refer to the official RE2 wiki page. If you’re looking for a quick start, check out the quick cheat sheet below—it’s more than enough to get you going.
| Construct | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
. | Any character | . |
| | Alternative | abc|def |
[ ] | Character class | [ghi] |
[^ ] | Negated character class (e.g., [^abc]) | [^jkl] |
[[: :]] | ASCII Character class | [[:alpha:]] |
[[:^ :]] | Negated ASCII Character class | [[:^space:]] |
( ) | Group a sub-expression | (mno)+ |
? | Preceding element is optional | p+ |
?? | Preceding element is optional (non-greedy) | q?? |
* | Preceding element is repeated zero or more times | r* |
*? | Preceding element is repeated zero or more times (non-greedy) | s*? |
+ | Preceding element is repeated one or more times | t+ |
+? | Preceding element is repeated one or more times (non-greedy) | u+? |
{ n } | Preceding element is repeated exactly n times | v{3} |
{ n, } | Preceding element is repeated at least n times | w{4,} |
{ n, }? | Preceding element is repeated at least n times (non-greedy) | x{5,}? |
{ n, m } | Preceding element is repeated from n to m times | y{6,7} |
{ n, m }? | Preceding element is repeated from n to m times (non-greedy) | z{8,9}? |
| Anchor | Description |
|---|---|
^ | Match at the beginning of line (or beginning of text) |
$ | Match at the end of line (or end of text) |
\A | Match at the beginning of text |
\z | Match at the end of text |
\b | Match at a word boundary |
\B | Match if not at a word boundary |
| Special character | Description |
|---|---|
\a | U+0007 — alarm character |
\e | U+001B — escape character |
\f | U+000C — formfeed character |
\n | U+000A — newline character |
\r | U+000D — carriage return character |
\t | U+0009 — tabulation character |
\v | U+000B — vertical tabulation character |
\* | U+002A — asterisk character (escape any special character with \ to match it literally) |
| Character code | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
\OOO | Character specified by three octal digits OOO | \033 |
\xHH | Character specified by two hexadecimal digits HH | \x1B |
\x{HHHHHH} | Character specified by hexadecimal digits HHHHHH (up to 10FFFF) | \x{25A1} |
| Perl character class | Description | Expands to |
|---|---|---|
\d | Decimal digits | [0-9] |
\D | Not decimal digits | [^0-9] |
\w | Word characters | [0-9A-Za-z_] |
\W | Not word characters | [^0-9A-Za-z_] |
\s | Whitespace | [\t\n\f\r ] |
\S | Not whitespace | [^\t\n\f\r ] |
| ASCII character class | Description | Expands to |
|---|---|---|
[[:alnum:]] | Alphanumeric | [0-9A-Za-z] |
[[:alpha:]] | Alphabetic | [A-Za-z] |
[[:ascii:]] | ASCII | [\x00-\x7F] |
[[:blank:]] | Blank | [\t ] |
[[:cntrl:]] | Control | [\x00-\x1F\x7F] |
[[:digit:]] | Decimal digits | [0-9] |
[[:graph:]] | Graphical | [!-~] |
[[:lower:]] | Lower case letters | [a-z] |
[[:print:]] | Printable | [ -~] |
[[:punct:]] | Punctuation | [!-/:-@[-`{-~] |
[[:space:]] | Whitespace | [\t\n\v\f\r ] |
[[:upper:]] | Upper case letters | [A-Z] |
[[:word:]] | Word characters | [0-9A-Za-z_] |
[[:xdigit:]] | Hexadecimal digits | [0-9A-Fa-f] |