SSH Channel
SSH Channel turns IO Ninja into a versatile SSH client. Use terminal view and work with your server like any other SSH client, or use IO Ninja’s extensive data handling capabilities provided in log view.
Basic Setup
In IO Ninja, click the “New Session” dropdown and select “SSH Channel”.
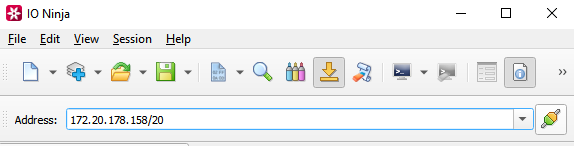
Enter the address of the server you want to connect to and press “Connect”.
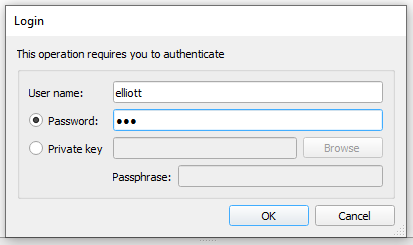
Enter your credentials and press “OK”.
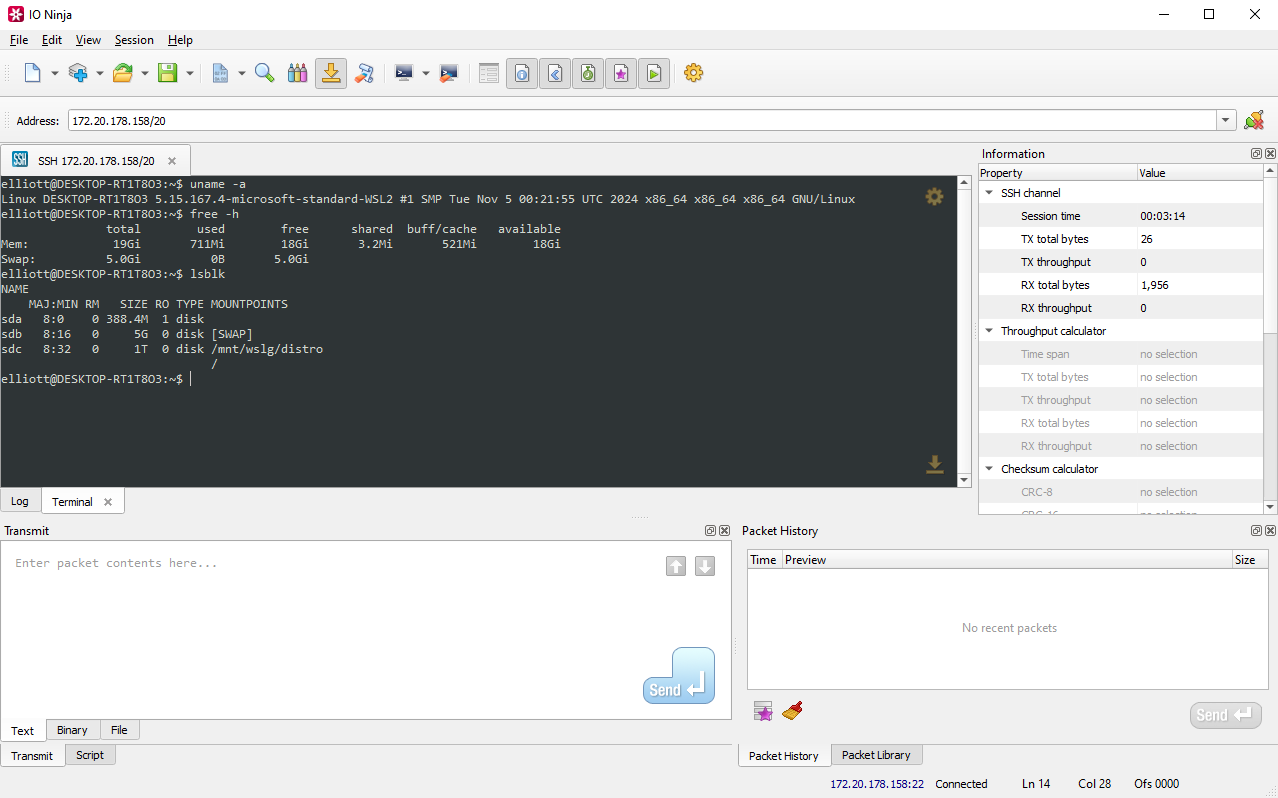
If required, press the “Show Terminal” button to enter terminal mode.
Note
Although this plugin can be used like any other SSH terminal, unlike all other SSH terminals, with IO Ninja you can inspect what’s actually being transmitted back and forth under the hood. The log shows all the intricate details, XTerm ESC codes, and raw byte streams, including control sequences, authentication handshakes, protocol-level negotiation data, and any anomalous or malformed packets that would otherwise be invisible in a conventional terminal emulator. If analyzing these logs could be useful for you, click the “Log” tab.
Adjust settings as needed via the “Settings” button (see “Settings” section below for details).
Settings
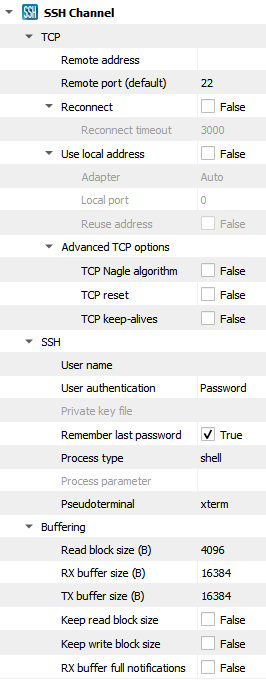
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
Remote address |
Remote address to connect to. Can be specified via IPv4 ( |
|
Remote port (default) |
Remote port to connect to in cases when a port is not explicitly specified in Remote address. |
80 |
Reconnect |
Attempt to reconnect when connection is dropped by the remote node. |
False |
Reconnect timeout |
The delay between reconnect attempts. |
3000 |
Use local address |
Bind socket to the specified local address. |
False |
Adapter |
Local network adapter to bind to. Pick one from the list of installed network adapters (or bind to all installed |
Auto |
Local port |
Local port to bind to. Setting this to |
8080 |
Reuse address |
Allow multiple sockets to share the same local address. Maps to the |
False |
TCP Nagle algorithm |
Delay transmission to reduce the number of small |
False |
TCP reset |
Drop TCP connections abruptly with a |
False |
TCP keep-alives |
Detect connection loss with |
False |
User name
|
User name for SSH authentication. |
|
User authentication
|
SSH authentication method (password or private key) |
Password |
Private key file
|
Private key file for SSH authentication (PEM format). |
|
Remember last password
|
Re-use the last entered password during subsequent connect attempts. |
True |
Process type
|
Type of requested SSH process. See available options. |
shell |
Process parameter
|
Parameter to pass to the remote process. |
|
Pseudoterminal
|
Type of requested pseudoterminal (PTY). Read more about psuedoterminal types here. |
xterm |
Read block size (B) |
The size of each individual read block submitted to the underlying transport. |
4KB |
RX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the incoming data ( |
16KB |
TX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the outbound data ( |
16KB |
Keep read block size |
Don’t merge read blocks in RX buffer. Incoming data blocks coming in quick succession can be merged together so that IO Ninja writes them to log as a whole. When this option is set to |
False |
Keep write block size |
Don’t merge write blocks in |
False |
RX buffer full notifications |
Toggle warnings in log about the incoming data ( |
False |
Process Type Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
shell |
Starts an interactive terminal session. Typing |
exec |
Runs a single command remotely (e.g., |
subsystem |
Launches a predefined service like SFTP (e.g., sftp user@host). |
Note
An example of an adapter dropdown on a typical Windows laptop is shown below: