Pcap Sniffer
Pcap Sniffer simplifies network traffic analysis by providing a streamlined, binary-friendly interface for capturing and inspecting raw packets. Built on the libpcap framework, it enhances traditional sniffing with a readable logging format and supports advanced testing through the injection of custom packets, making it a versatile tool for diagnostics, protocol analysis, and security evaluation.
Basic Setup
In IO Ninja, click the “New Session” dropdown and select “Pcap Sniffer”.
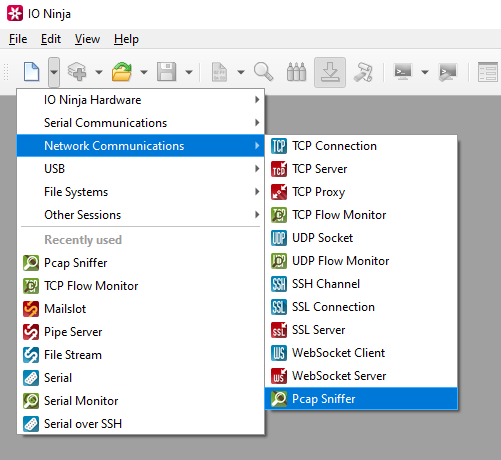
In the “Filter:” field, type a view filter, e.g. “port 137”.
Note
For more information on pcap filters, please see the official documentation.
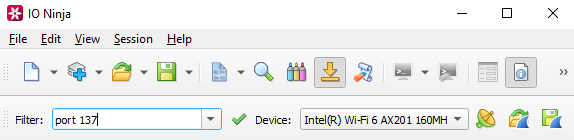
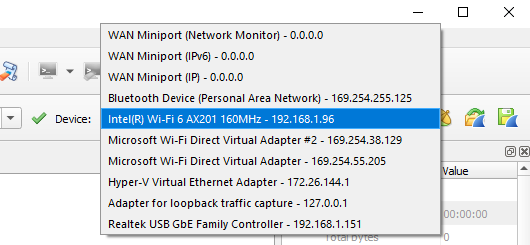
Select your network interface from “Device:”.
Click the “Capture” button to the right of the “Device:” dropdown to start capturing traffic.
Note
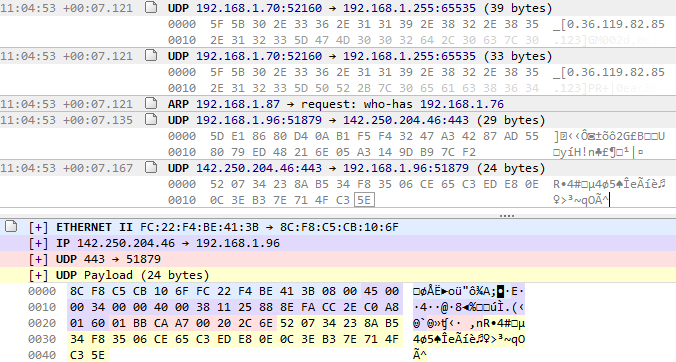
Unlike most other plugins, Pcap Sniffer features two log panes, the standard log, and the Log Detail Pane, which provides an in-depth, context-sensitive view of the packet selected in the Main Log Pane. It breaks down the entire protocol stack, such as Ethernet, IP, and UDP, displaying each header and its fields with clearly labeled values. It also presents the raw payload in both hexadecimal and ASCII formats, with color-coding that visually distinguishes protocol layers. This pane is essential for deep packet inspection, allowing users to verify exact field contents, troubleshoot communication issues, inspect for security concerns, or analyze the structure of custom or application-layer protocols at the byte level.
Use the transmit pane to inject packets.
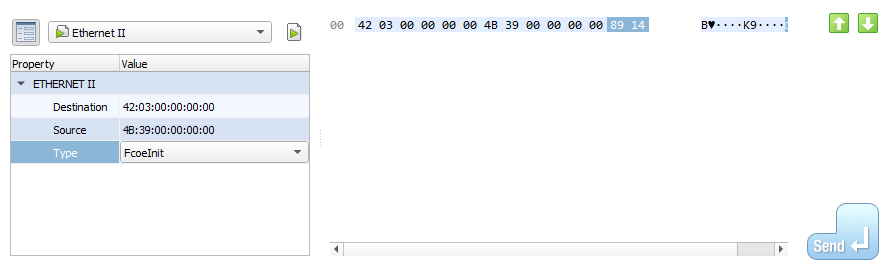
Note
Packet templates are available for core protocols (with auto-calculation of checksums and all the other benefits of our packet templates).
Adjust settings as needed via the “Settings” button (see “Settings” section below for details).
Settings
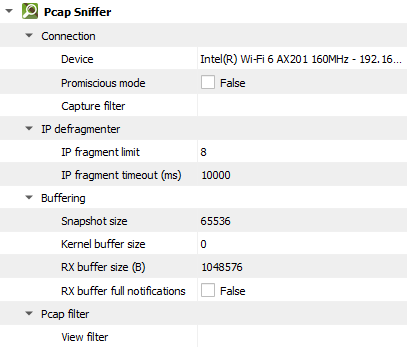
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
Device |
The device to capture. |
|
Promiscious mode |
Promiscuous mode allows the capture of all packets on the network segment, regardless of their destination MAC address. This includes packets not addressed to the host machine, enabling comprehensive traffic analysis. |
False |
Capture filter |
Term to filter with when capturing packets. For more information on pcap filters, please see the official documentation. |
|
IP fragment limit |
The maximum number of IP fragments. IP fragments refer to the pieces of a larger IP packet that has been broken up for transmission across a network. IP datagrams can be fragmented during transmission, and the Pcap Sniffer attempts to reassemble these fragments into complete packets. To do this, it maintains a database of observed fragments. However, if the network contains malformed or maliciously crafted fragments, the defragmentation process can be overwhelmed. To prevent this, the analyzer applies several sanity checks. For example, incomplete fragment chains are discarded after a timeout to avoid indefinite retention, and the number of fragments in a chain is limited—since it’s highly unlikely that a legitimate IP datagram would be split into more than a few parts. By enforcing these limits, the analyzer can effectively discard suspicious or malformed chains, making the defragmentation process more robust and secure in hostile network environments. |
8 |
IP fragment timeout (ms) |
The maximum delay between IP fragments. |
10000 |
Snapshot size |
Pcap (packet capture) snapshot size. The snapshot size is the maximum number of bytes per packet that the capture tool will store in the capture buffer. |
65536 |
Kernel buffer size |
Pcap (packet capture) kernel buffer size. Kernel buffer is a memory space allocated in the OS kernel to temporarily store packets that arrive on the network interface before they are handed over to an application. A value of |
0 |
RX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the incoming data ( |
1048576 |
RX buffer full notifications |
Toggle warnings in log about the incoming data ( |
False |
View filter |
Term to filter with when displaying packets. For more information on pcap filters, please see the official documentation. |
Note
“Capture filter” filters what is captured, while “View filter” filters the log after capturing. Only use “Capture filter” if you are sure that you will not later need the packets that you are filtering out. If you may need the packets later, capture everything and filter using the “View filter”.