Serial
The Serial plugin for IO Ninja is a powerful, versatile serial terminal designed for embedded developers, hardware engineers, and IoT enthusiasts. It supports text and binary data views, interleaves serial events with data for a complete timeline, and includes advanced features like regex colorization, real-time checksum calculations, and customizable packet templates.
Basic Setup
Ensure your serial device is connected to the computer that is running IO Ninja.
In IO Ninja, click the “New Session” dropdown and select a new “Serial” session.
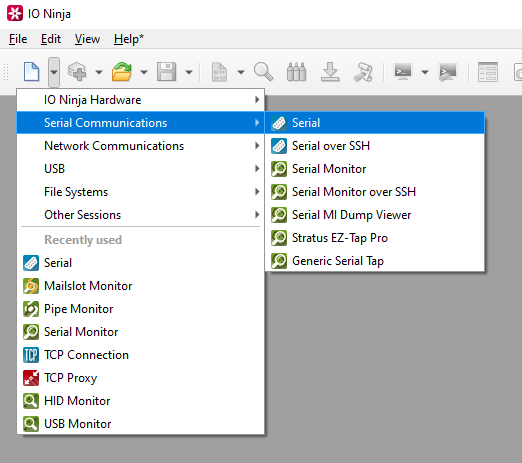
If not selected automatically, select your serial device from the “Port:” dropdown.
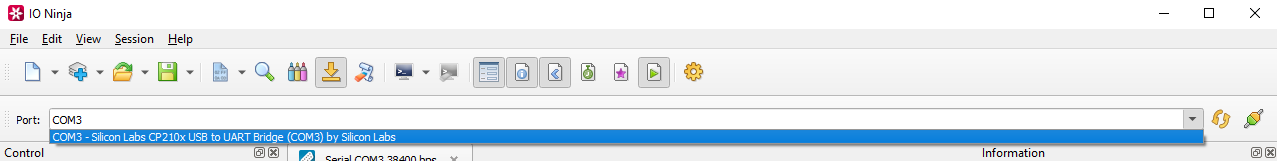
Open the port by clicking the “Open” button located to the right of the “Port:” dropdown.

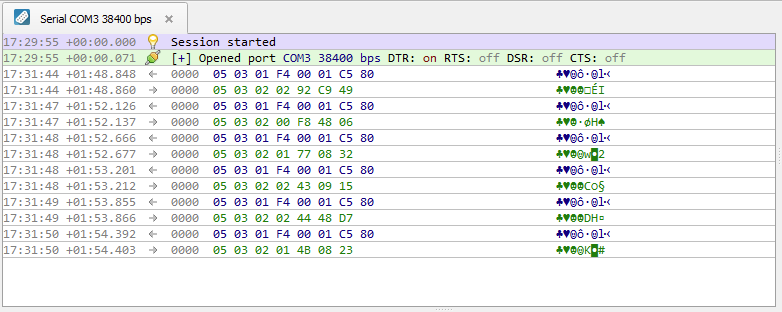
Monitor traffic in the “Serial” window.
Adjust settings as needed via the “Settings” button (see “Settings” section below for details).
Craft Serial Packets
In the “Transmit” pane, type your binary packet and press “Send”.

Settings
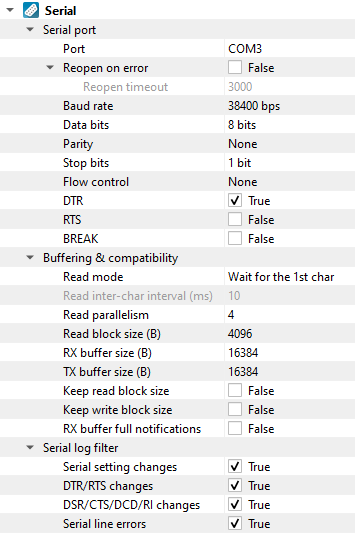
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
Port |
The port that should be used. |
|
Reopen on error |
Attempt to re-open port if disconnected on error, e.g., due to manual unplug of USB-to-Serial device. |
False |
Reopen timeout |
Delay to insert between re-open attempts. |
3000 |
Baud rate |
The serial baud rate. |
38400 bps |
Data bits |
Serial data bit count (word size). See available options. |
8 bits |
Parity |
Serial parity check type. See available options. |
None |
Stop bits |
Serial stop bit count. See available options. |
1 bit |
Flow control |
Serial flow control. See available options. |
None |
DTR |
State of the DTR (Data-Terminal-Ready) modem control line. |
True |
RTS |
State of the RTS (Request-to-Send) modem control line. |
False |
BREAK |
Enable the BREAK condition on the TX line. |
False |
Read mode
(Windows-only)
|
Advanced read request-specific options. See available options. |
Wait for the 1st char |
Read inter-char interval (ms)
(Windows-only)
|
Maximum inter-character delay during read request. |
10 |
Read parallelism
(Windows-only)
|
Maximum number of read requests to issue in parallel. Having more than one pending read at a time helps with increasing read throughput when incoming data arrives in rapid streams (after filling one user buffer, the kernel can immediately switch to the next one without any waiting). Increasing this number beyond 4 usually won’t yield any extra performance gains. |
4 |
Read block size (B) |
The size of each individual read block submitted to the underlying transport. |
4KB |
RX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the incoming data (RX) buffer. Affects read throughput. |
16KB |
TX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the outbound data (TX) buffer. Affects write throughput.. |
16KB |
Keep read block size |
Don’t merge read blocks in RX buffer. Incoming data blocks coming in quick succession can be merged together so that IO Ninja writes them to log as a whole. When this option is set to |
False |
Keep write block size |
Don’t merge write blocks in TX buffer. Outbound data blocks sent in quick succession can be merged together before submission to the underlying transport. When this option is set to |
False |
RX buffer full notifications |
Toggle warnings in log about the incoming data (RX) buffer getting full. |
False |
Serial setting changes |
Toggle notifications about serial setting (baud rate, data size, parity, stop bits, flow control) changes in the log. |
on |
DTR/RTS changes |
Toggle notifications about control line ( |
on |
DSR/CTS/DCD/RI changes |
Toggle notifications about status line ( |
on |
Serial line errors |
Toggle warning about serial line errors ( |
on |
Data Bit Options
Option |
|---|
5 bits |
6 bits |
7 bits |
8 bits |
Parity Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
None |
No parity bit is used |
Odd |
Odd parity (parity bit is set when the number of logical ones in the UART frame is odd). |
Even |
Even parity (parity bit is set when the number of logical ones in the UART frame is even). |
Mark |
Parity bit is present and always set. |
Space |
Parity bit is present and always clear. |
Stop Bit Options
Option |
|---|
1 bit |
1.5 bits |
2 bits |
Flow Control Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
None |
No flow control. |
RTS/CTS |
Hardware flow control using CTS and RTS lines. |
XON/XOFF |
Software flow control using XON and XOFF lines. |
Read Mode Options (Windows-only)
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Check COMSTAT.cbInQue |
Prior to reading, check the status of the incoming buffer of the serial driver. Only read the number of bytes available there. |
Wait for the 1st character |
Read requests return as soon as possible (as soon as at least one byte arrives). |
Interval-based |
Read requests keep accumulating bytes until the inter-character delay exceeds the limit specified by “Read inter-char interval (ms)” or the buffer is full. |
Note
Typically, it’s best to leave the Read Mode setting at its default (Wait for the 1st character), unless compatibility issues require a change. The default setting is optimal in most situations.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. How can I automatically append line ending characters?
Appending line ending characters is easily achieved using the TX Modifier Layer plugin.
To automatically append line endings:
Add the TX Modifier layer to your serial session.
In the layer settings, enable the Append suffix option.
Enter the desired suffix (e.g.,
\r\n) in the configuration.
This will automatically add your specified line endings to all outgoing transmissions—saving you from typing them manually each time. The TX Modifier layer also supports many other advanced transformations, but you can keep it simple if you only need suffixes.
IO Ninja timestamps entire data blocks as they are received from the operating system, not individual bytes. Since bytes within a block arrive in quick succession, the block timestamp provides a reliable indication of when the data was received. Although you cannot assign timestamps to each CR-terminated line directly, the existing timestamps offer millisecond-level accuracy and can be exported for use in test or simulation systems.