I2C/SPI Tap
Note
This page is for the I2C/SPI Tap Tap plugin. For the board, see the hardware docs.
The I2C/SPI Tap for IO Ninja is a hardware sniffer for monitoring I2C and SPI communications. Our sniffer allows you to tap into the lines of I2C and SPI links and immediately view the captured data bytes in IO Ninja software — in real time and using our innovative dual-hex view tailor-suited for the inherently full-duplex SPI data. Use this plugin to monitor all communications.
Basic Setup
Ensure your I2C/SPI Tap is connected to your computer.
Please see the hardware documentation for guidance on doing so.
In IO Ninja, click the “New Session” dropdown and select a new “I2C/SPI Tap” session.
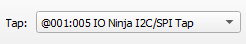
If not selected automatically, select your I2C/SPI Tap from the “Tap:” dropdown.
Note
If you can’t see your tap, press the “Refresh” button.
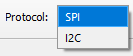
Select either “SPI” or “I2C” from the “Protocol:” dropdown.
Start capturing by clicking the “Capture” button located to the right of the “Protocol:” dropdown.

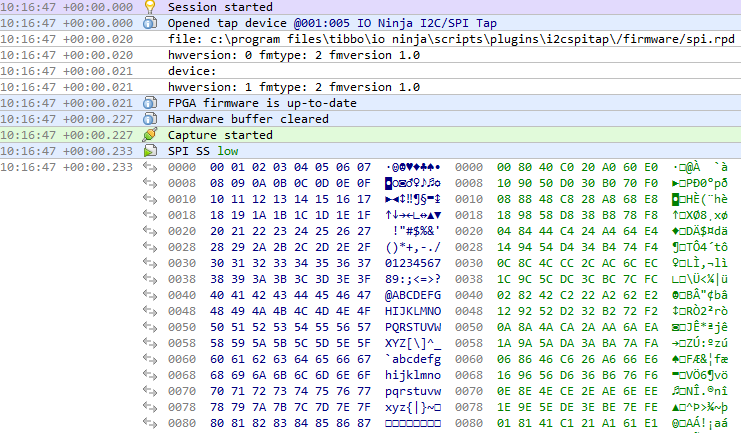
Monitor communications in the “I2C/SPI Tap” tab.
Adjust settings as needed via the “Settings” button (see “Settings” section below for details).
Settings
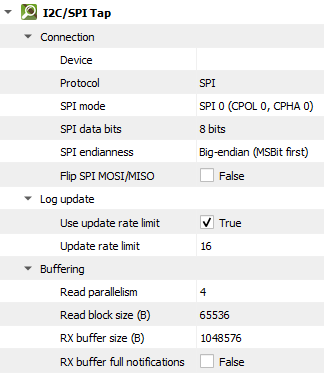
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
Tap |
The I2C/SPI Tap that should be used. |
|
Protocol |
The protocol to be used, either |
SPI |
SPI mode |
Determines when data is sampled and shifted based on the clock polarity ( |
SPI-0 (CPOL 0, CPHA 0) |
SPI data bits |
Number of bits sent in each transaction from master to slave (or vice versa). See available options. |
8 bits |
SPI endianness |
The order in which individual bits within a byte or word are transmitted on the data line. See available options. |
Big-endian (MSBit first) |
Flip SPI MOSI/MISO |
Flip the |
False |
Use update rate limit |
Only allow a specified number of log scroll operations per second. |
True |
Update rate limit |
The number of log scroll operations allowed per second. |
16 |
Read parallelism
(Windows-only)
|
Maximum number of read requests to issue in parallel. Having more than one pending read at a time helps with increasing read throughput when incoming data arrives in rapid streams (after filling one user buffer, the kernel can immediately switch to the next one without any waiting). Increasing this number beyond 4 usually won’t yield any extra performance gains. |
4 |
Read block size (B) |
The size of each individual read block submitted to the underlying transport. |
4KB |
RX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the incoming data ( |
16KB |
Keep read block size |
Don’t merge read blocks in RX buffer. Incoming data blocks coming in quick succession can be merged together so that IO Ninja writes them to log as a whole. When this option is set to |
False |
RX buffer full notifications |
Toggle warnings in log about the incoming data ( |
False |
SPI Mode Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
SPI-0 (CPOL 0, CPHA 0) |
Clock starts low, data is read on rising edge. |
SPI-1 (CPOL 0, CPHA 1) |
Clock starts low, data is read on falling edge. |
SPI-2 (CPOL 1, CPHA 0) |
Clock starts high, data is read on falling edge. |
SPI-3 (CPOL 1, CPHA 1) |
Clock starts high, data is read on rising edge. |
SPI Data Bit Options
Option |
|---|
4 bits |
8 bits |
12 bits |
16 bits |
SPI Endianness Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Little-endian (LSBit first) |
The least significant bit is transmitted first, meaning data is shifted out starting with the rightmost bit. This is less common and typically used only when a specific device requires it. |
Big-endian (MSBit first) |
The most significant bit is transmitted first, starting with the leftmost bit of the byte or word. This is the standard and most widely used format in SPI communications. |