Generic Serial Tap
The Generic Serial Tap plugin should be used together with a dual-COM serial tap device, such as EZ-Tap RS-232 from Stratus Engineering Inc. Alternatively, you can easily solder your own tap.
The idea is to read all the lines of an ongoing serial (RS-232/RS-422/RS-485) communications using a pair of auxiliary “spy” serial links. A pair is needed because half of the lines (TX, DTR and RTS) can only be written to — so we need yet another connection to read those, as well.
After everything is connected, you can follow the steps below to start monitoring inside IO Ninja.
Basic Setup
In IO Ninja, click the “New Session” dropdown and select a new “Generic Serial Tap” session.
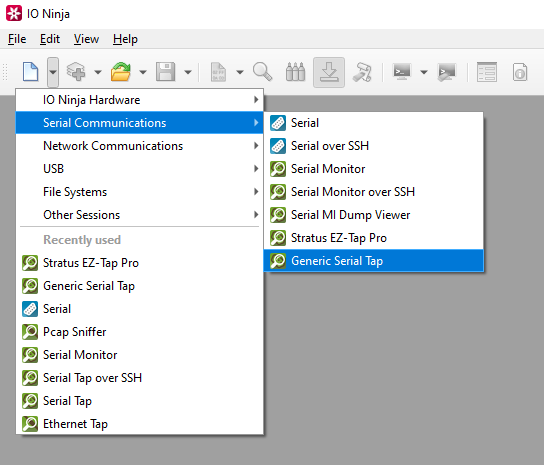
In the DTE and DCE fields, select the ports for your pair of auxiliary “spy” serial links.
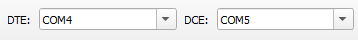
Start capturing by clicking the “Capture” button.

Monitor traffic in the log.
Adjust settings as needed via the “Settings” button (see “Settings” section below for details).
Settings
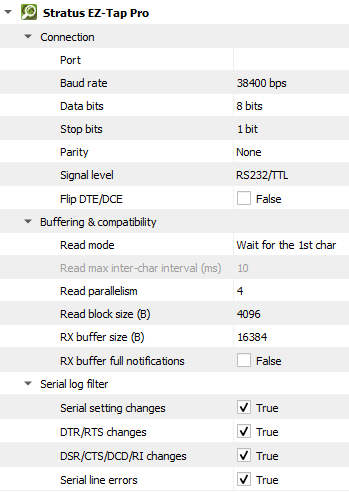
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
DTE |
Specify a DTE serial port to monitor. |
|
DCE |
Specify a DCE serial port to monitor. |
|
Baud rate |
The serial baud rate. |
38400 bps |
Data bits |
Serial data bit count (word size). See available options. |
8 bits |
Parity |
Serial parity check type. See available options. |
None |
Stop bits |
Serial stop bit count. See available options. |
1 bit |
Flip DTE/DCE |
Flip logical sides of the tap cable. |
False |
Read mode
(Windows-only)
|
Advanced read request-specific options. See available options. |
Wait for the 1st char |
Read max inter-char interval (ms) |
Maximum inter-character delay during read request. |
10 |
Read parallelism
(Windows-only)
|
Maximum number of read requests to issue in parallel. Having more than one pending read at a time helps with increasing read throughput when incoming data arrives in rapid streams (after filling one user buffer, the kernel can immediately switch to the next one without any waiting). Increasing this number beyond 4 usually won’t yield any extra performance gains. |
4 |
Read block size (B) |
The size of each individual read block submitted to the underlying transport. |
4KB |
RX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the incoming data ( |
16KB |
Keep read block size |
Don’t merge read blocks in RX buffer. Incoming data blocks coming in quick succession can be merged together so that IO Ninja writes them to log as a whole. When this option is set to |
False |
RX buffer full notifications |
Toggle warnings in log about the incoming data ( |
False |
Serial setting changes |
Toggle notifications about serial setting (baud rate, data size, parity, stop bits, flow control) changes in the log. |
on |
DTR/RTS changes |
Toggle notifications about control line ( |
on |
DSR/CTS/DCD/RI changes |
Toggle notifications about status line ( |
on |
Serial line errors |
Toggle warning about serial line errors ( |
on |
Data Bit Options
Option |
|---|
5 bits |
6 bits |
7 bits |
8 bits |
Parity Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
None |
No parity bit is used |
Odd |
Odd parity (parity bit is set when the number of logical ones in the UART frame is odd). |
Even |
Even parity (parity bit is set when the number of logical ones in the UART frame is even). |
Mark |
Parity bit is present and always set. |
Space |
Parity bit is present and always clear. |
Stop Bit Options
Option |
|---|
1 bit |
1.5 bits |
2 bits |
Read Mode Options (Windows-only)
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Check COMSTAT.cbInQue |
Prior to reading, check the status of the incoming buffer of the serial driver. Only read the number of bytes available there. |
Wait for the 1st character |
Read requests return as soon as possible (as soon as at least one byte arrives). |
Interval-based |
Read requests keep accumulating bytes until the inter-character delay exceeds the limit specified by “Read inter-char interval (ms)” or the buffer is full. |
Note
Typically, it’s best to leave the Read Mode setting at its default (Wait for the 1st character), unless compatibility issues require a change. The default setting is optimal in most situations.