Serial Tap over SSH
The Serial Tap over SSH plugin extends the power of the IO Ninja Serial Tap to remote Linux devices, enabling monitoring of serial ports on machines like headless Raspberry Pi boards.
Basic Setup
Prerequisites
Enabling SSH
On most Linux machines, SSH is enabled by default. However, if it is not, you will need to enable it.
On Raspbian and many other popular distros, you can perform the following command:
systemctl enable --now sshd
For other Linux distributions, please refer to their documentation.
Installing the Hardware Client
The Serial Tap over SSH plugin uses the IO Ninja Hardware Client (ioninja-hwc).
This hardware client needs to be installed and configured on the remote machine.
Note
See Installing the Hardware Client for instructions.
Serial SSH’ing into your Linux Machine with IO Ninja
In IO Ninja, click the “New Session” dropdown and select a new “Serial Tap over SSH” session.
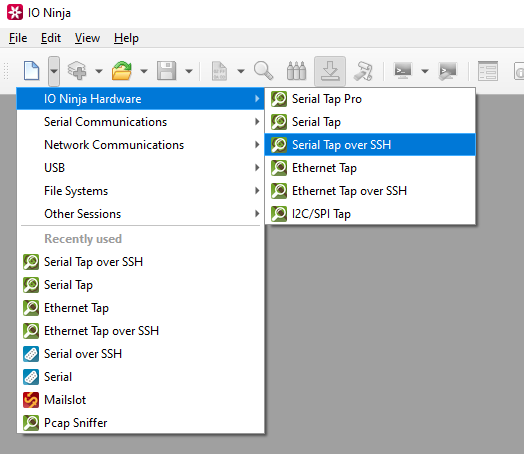
Type the host address of your remote Linux machine into the “Address:” field.
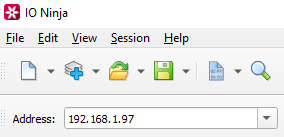
Adjust settings as needed via the “Settings” button (see “Settings” section below for details).
Note
Many of these settings are also available in the “Control” pane for easy access.
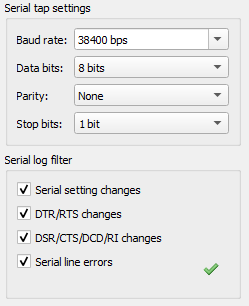
Note
Before capturing, you should select the proper baud rate (and other serial parameters).
Click the “Capture” button to the right of the “Address:” field to initiate a connection.
Note
You will be prompted for SSH credentials.
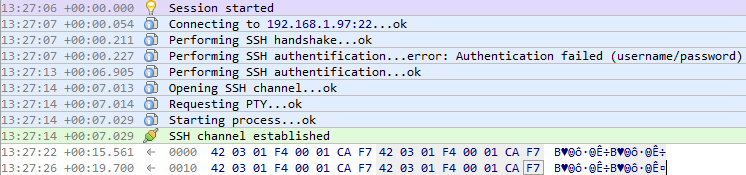
Monitor your Serial Communications as Usual
See all communications in the Ninja Scroll Engine.
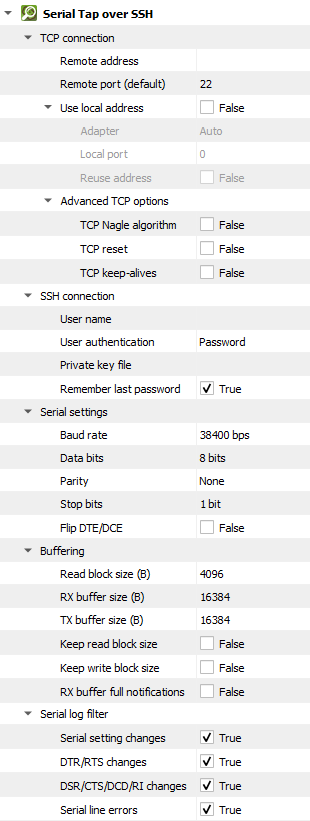
Settings
Setting |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
Remote address |
Remote address to connect to. Can be specified via IPv4 ( |
|
Remote port (default) |
Remote port to connect to in cases when a port is not explicitly specified in Remote address. |
80 |
Use local address |
Bind socket to the specified local address. |
False |
Adapter |
Local network adapter to bind to. Pick one from the list of installed network adapters (or bind to all installed |
Auto |
Local port |
Local port to bind to. Setting this to |
8080 |
Reuse address |
Allow multiple sockets to share the same local address. Maps to the |
False |
TCP Nagle algorithm |
Delay transmission to reduce the number of small |
False |
TCP reset |
Drop TCP connections abruptly with a |
False |
TCP keep-alives |
Detect connection loss with |
False |
User name
|
User name for SSH authentication. |
|
User authentication
|
SSH authentication method (password or private key) |
Password |
Private key file
|
Private key file for SSH authentication (PEM format). |
|
Remember last password
|
Re-use the last entered password during subsequent connect attempts. |
True |
Baud rate |
The serial baud rate. |
38400 bps |
Data bits |
Serial data bit count (word size). See available options. |
8 bits |
Parity |
Serial parity check type. See available options. |
None |
Stop bits |
Serial stop bit count. See available options. |
1 bit |
Flip DTE/DCE |
Flip logical sides of the tap cable. All serial lines can be split into |
False |
Read block size (B) |
The size of each individual read block submitted to the underlying transport. |
4KB |
RX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the incoming data ( |
16KB |
TX buffer size (B) |
The full size of the outbound data ( |
16KB |
Keep read block size |
Don’t merge read blocks in RX buffer. Incoming data blocks coming in quick succession can be merged together so that IO Ninja writes them to log as a whole. When this option is set to |
False |
Keep write block size |
Don’t merge write blocks in |
False |
RX buffer full notifications |
Toggle warnings in log about the incoming data ( |
False |
Serial setting changes |
Toggle notifications about serial setting (baud rate, data size, parity, stop bits, flow control) changes in the log. |
on |
DTR/RTS changes |
Toggle notifications about control line ( |
on |
DSR/CTS/DCD/RI changes |
Toggle notifications about status line ( |
on |
Serial line errors |
Toggle warning about serial line errors ( |
on |
Data Bit Options
Option |
|---|
5 bits |
6 bits |
7 bits |
8 bits |
Parity Options
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
None |
No parity bit is used |
Odd |
Odd parity (parity bit is set when the number of logical ones in the UART frame is odd). |
Even |
Even parity (parity bit is set when the number of logical ones in the UART frame is even). |
Mark |
Parity bit is present and always set. |
Space |
Parity bit is present and always clear. |
Stop Bit Options
Option |
|---|
1 bit |
1.5 bits |
2 bits |